Introduction
In today’s fast-paced world, stress has become an inevitable companion for many. From bustling cities to academic pressures, individuals often find themselves overwhelmed. One of the most effective yet overlooked solutions to combat stress is quality sleep. This article delves into the intricate relationship between sleep and stress, emphasizing the importance of good sleep hygiene, and provides actionable strategies to enhance sleep quality, thereby reducing stress levels.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Link Between Sleep and Stress
- The Science Behind Sleep and Stress
- Impact of Poor Sleep on Stress Levels
- Strategies to Improve Sleep Quality
4.1 Establishing a Consistent Sleep Schedule
4.2 Creating a Restful Sleep Environment
4.3 Limiting Stimulants and Screen Time
4.4 Incorporating Relaxation Techniques - The Role of Diet and Exercise in Sleep Quality
- Seeking Professional Help
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Understanding the Link Between Sleep and Stress
Sleep and stress share a bidirectional relationship. While stress can impede sleep quality, poor sleep can exacerbate stress levels. This cycle can lead to a detrimental impact on overall well-being. Recognizing this connection is the first step toward managing both effectively.

The Science Behind Sleep and Stress
During sleep, the body undergoes various restorative processes. Adequate sleep allows the brain to process emotions and consolidate memories, which are essential for emotional regulation. Conversely, insufficient sleep can lead to heightened emotional reactivity, making individuals more susceptible to stress.
Impact of Poor Sleep on Stress Levels
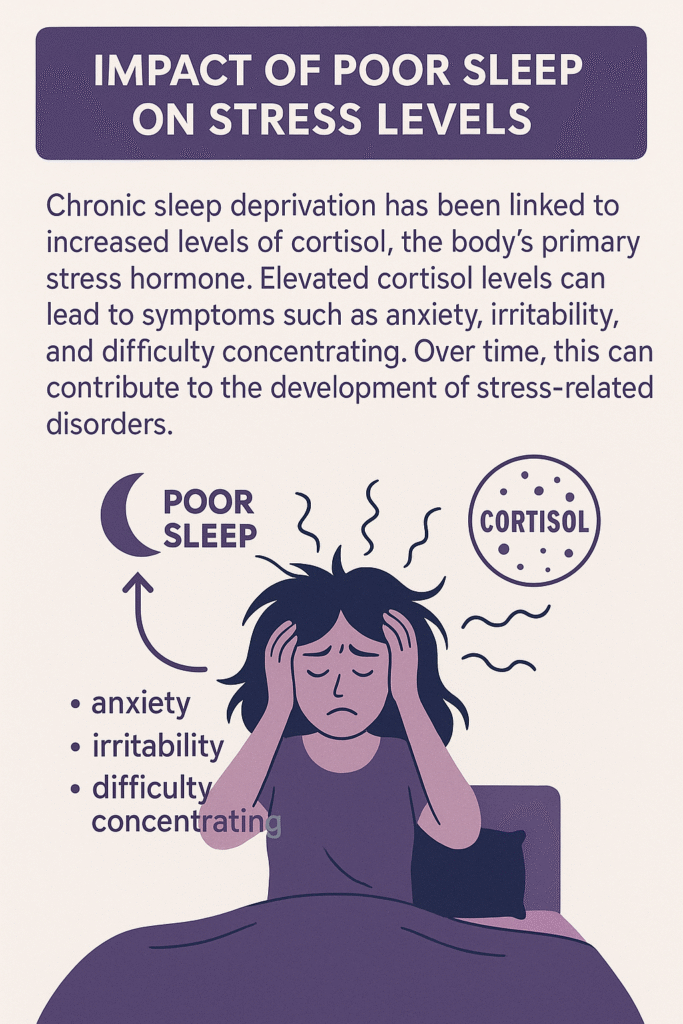
Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to increased levels of cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone. Elevated cortisol levels can lead to symptoms such as anxiety, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. Over time, this can contribute to the development of stress-related disorders.
Strategies to Improve Sleep Quality
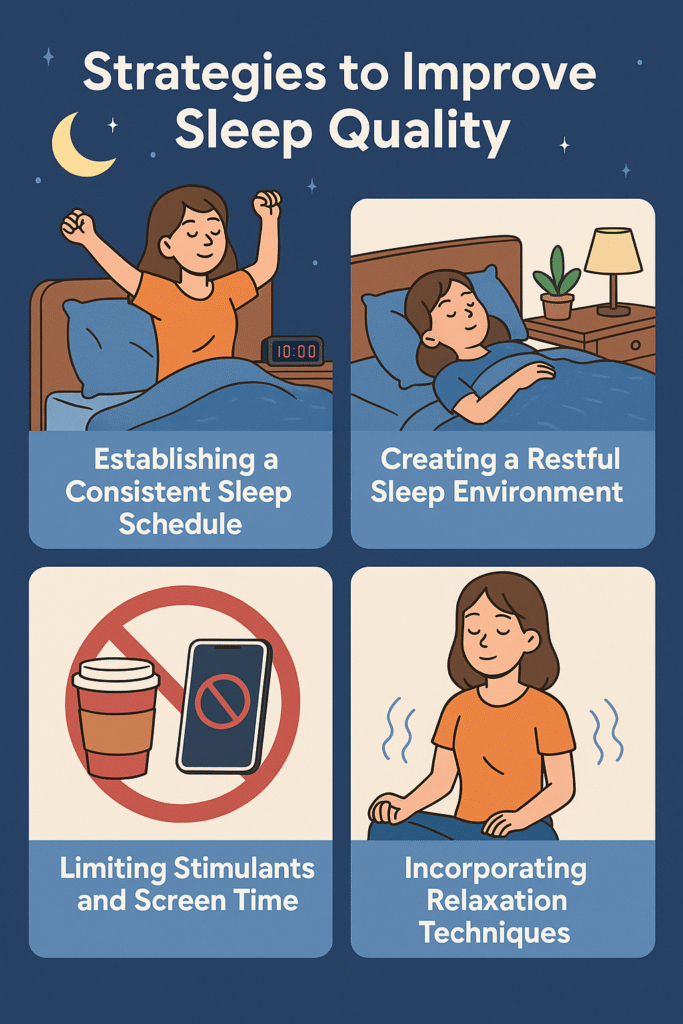
4.1 Establishing a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate the body’s internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up naturally. Consistency reinforces the body’s sleep-wake cycle, leading to improved sleep quality.

4.2 Creating a Restful Sleep Environment
A conducive sleep environment is crucial for quality rest. Ensure the bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. Investing in a comfortable mattress and pillows can also make a significant difference in sleep quality.
4.3 Limiting Stimulants and Screen Time
Avoid consuming caffeine or nicotine close to bedtime, as these substances can interfere with the ability to fall asleep. Additionally, the blue light emitted by screens can disrupt melatonin production, a hormone essential for sleep. Limiting screen time before bed can promote better sleep.
4.4 Incorporating Relaxation Techniques
Practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help calm the mind and prepare the body for sleep. Engaging in these activities before bedtime can reduce stress and improve sleep quality.
The Role of Diet and Exercise in Sleep Quality
Regular physical activity can promote faster sleep onset and deeper sleep. However, exercising too close to bedtime may have the opposite effect. Regarding diet, consuming a heavy meal right before bed can lead to discomfort and indigestion, hindering sleep. Opting for light snacks that promote sleep, such as those rich in tryptophan, can be beneficial.
Seeking Professional Help
If sleep disturbances persist despite implementing these strategies, it may be time to consult a healthcare professional. Conditions like insomnia or sleep apnea require medical intervention. A healthcare provider can offer tailored treatments to address underlying issues.
Conclusion
Quality sleep is a cornerstone of stress management. By understanding the interplay between sleep and stress and adopting strategies to enhance sleep quality, individuals can break the cycle of stress and poor sleep, leading to improved overall health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How many hours of sleep do adults need?
A1: Adults typically require 7–9 hours of sleep per night for optimal health.
Q2: Can napping during the day affect nighttime sleep?
A2: While short naps can be refreshing, long or late-afternoon naps can interfere with nighttime sleep.
Q3: Is it normal to have trouble sleeping occasionally?
A3: Occasional sleeplessness is common and can be due to temporary stressors. However, persistent sleep issues should be addressed.
Q4: Can stress cause sleep disorders?
A4: Yes, chronic stress can lead to sleep disorders such as insomnia.
Q5: Are there foods that promote better sleep?
A5: Yes, foods like cherries, bananas, and oats contain melatonin and can promote better sleep.
NOTE:
By implementing the strategies outlined above, individuals can improve their sleep quality, thereby reducing stress levels and enhancing overall health. Remember, the journey to better sleep begins with understanding and making informed choices.
